I’m an astrophysicist working at the University of Oxford as a Royal Society URF.
My research is at the intersection of theory and observation and my interests are fairly broad, but fundamentally I am interested in the extreme
and exotic physics that can be probed using accreting black holes and the outflows they produce.
In particular, my work focuses on the origins
of the highest energy cosmic rays, the physics of accretion disc winds, the disc-wind-jet connection in AGN and X-ray binaries, and the hydrodynamics of astrophysical jets on all scales.
More recently, I have started using X-ray observations of cluster-hosted AGN to search for, and place limits on, axion-like particles,
which are exotic dark matter candidates.
Some (fairly) recent highlights can be found below, together with a list of current projects, publications and talks.
If you have any questions, please get in touch. You can also read my PhD thesis
or CV.
james.matthews [at] physics [dot] ox [dot] ac [dot] uk
Oxford Astrophysics
The Denys Wilkinson Building,
Keble Road,
Oxford
OX1 3RH

The public release of the Sirocco Monte Carlo radiative transfer and photoionization code, together with its documentation and the code release paper.
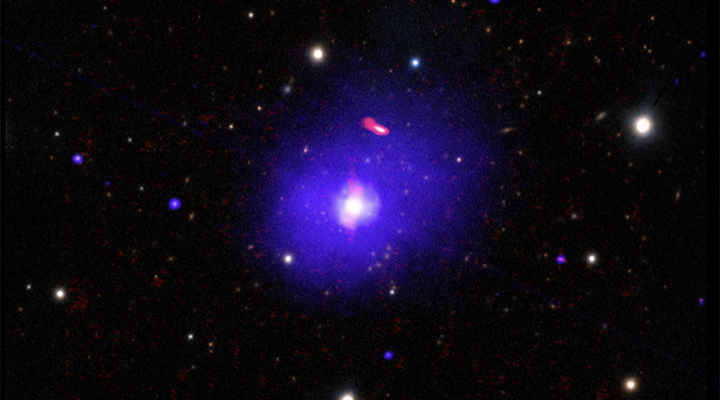

Chandra Shows Giant Black Hole Spins Slower Than Its Peers
A recent NASA press release from a paper led by Julia Sisk-Reynes, an IoA PhD student.

A new code I wrote to solve the axion-photon conversion problem, and an accompanying paper
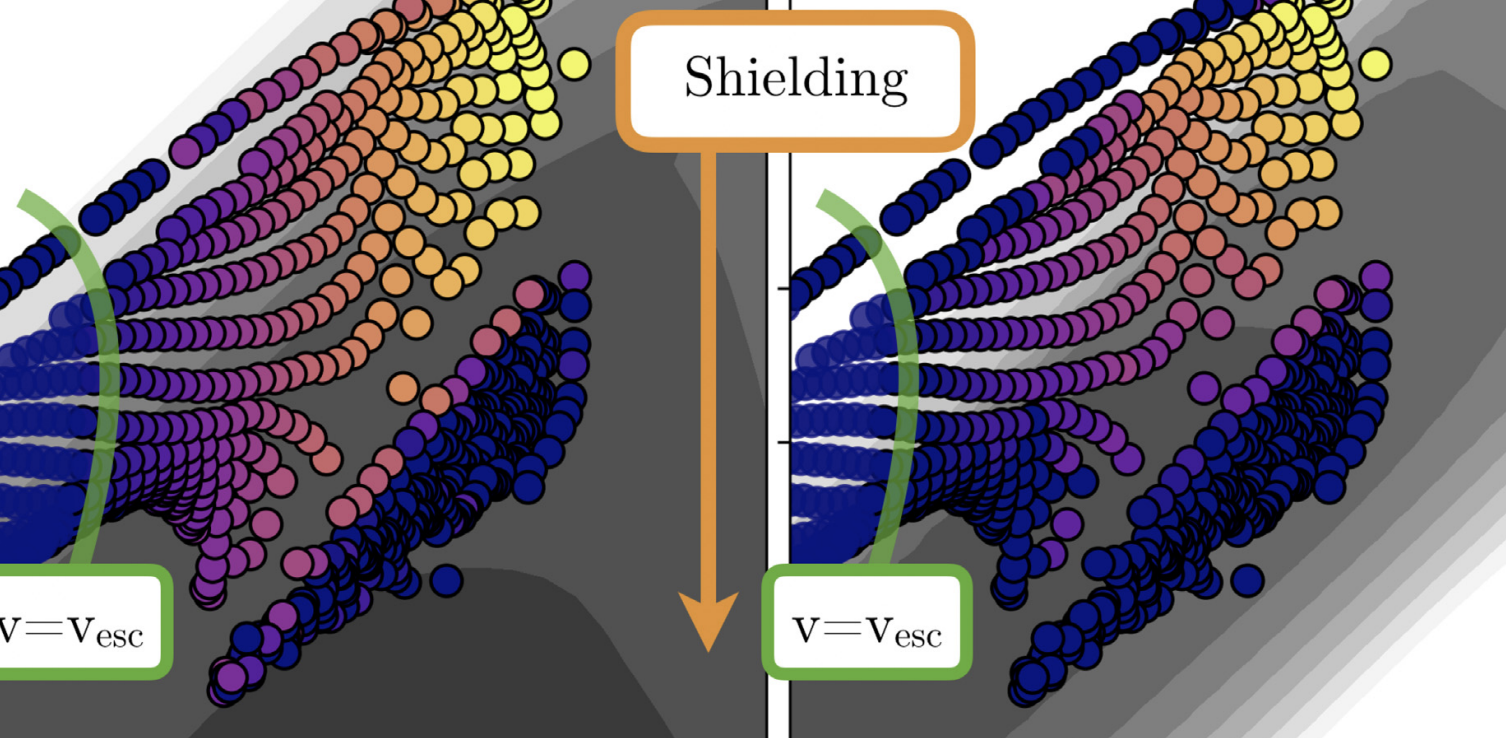
A disc wind model for quasar emission line blueshifts
A 2023 paper, which uses SIROCCO to construct a disc wind model for quasar emission line blueshifts and accompanying data and code.
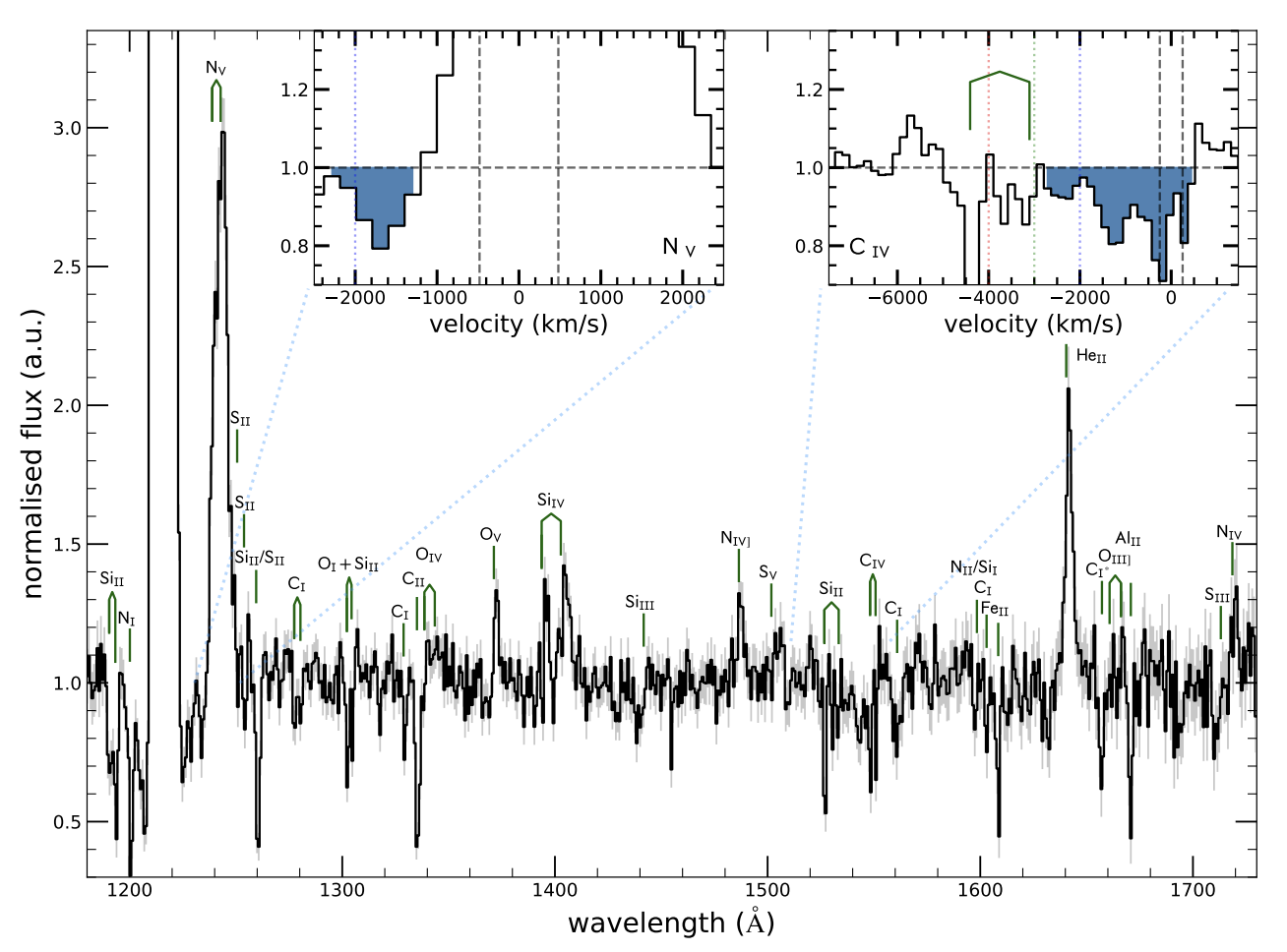
UV and Optical Disc Winds in X-ray Binaries
Two results from the past few years:
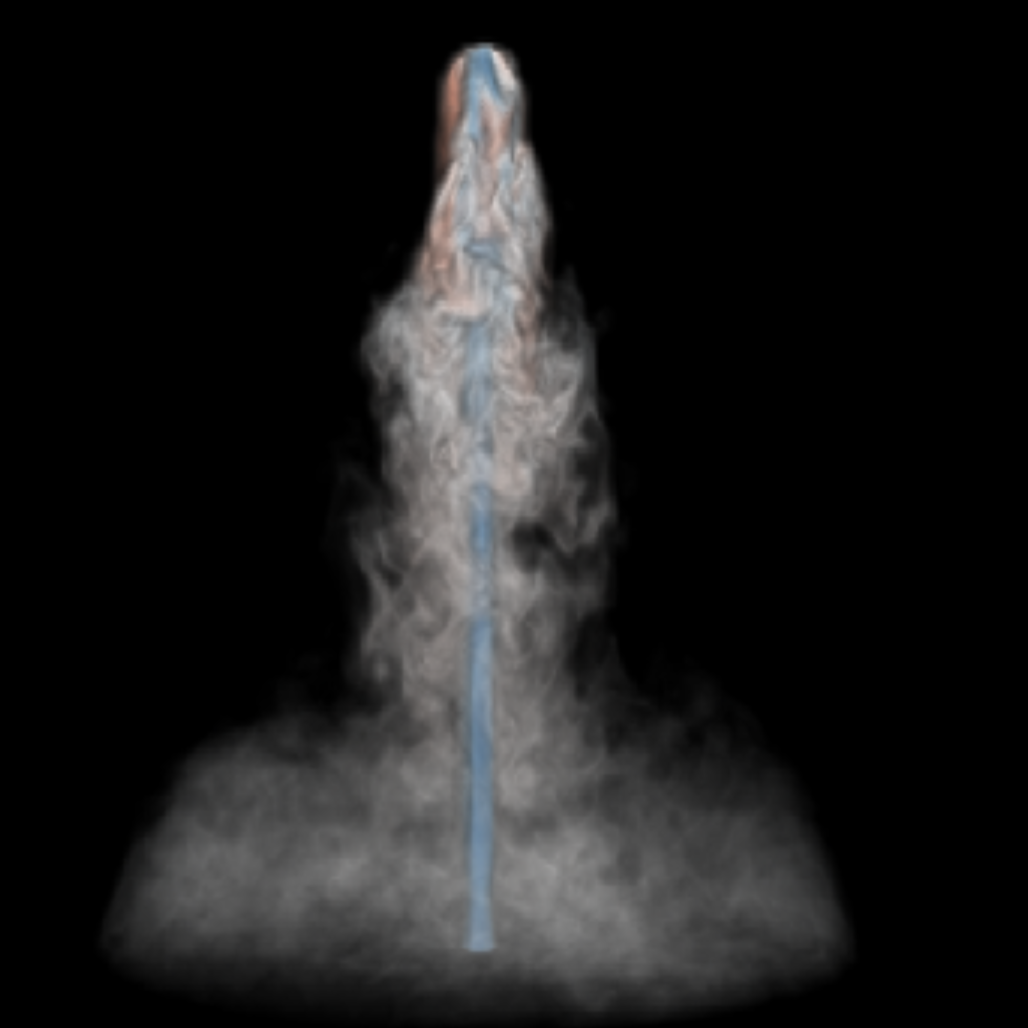
Information and movies from a recent paper about UHECRs from shocks in the lobes of radio galaxies.
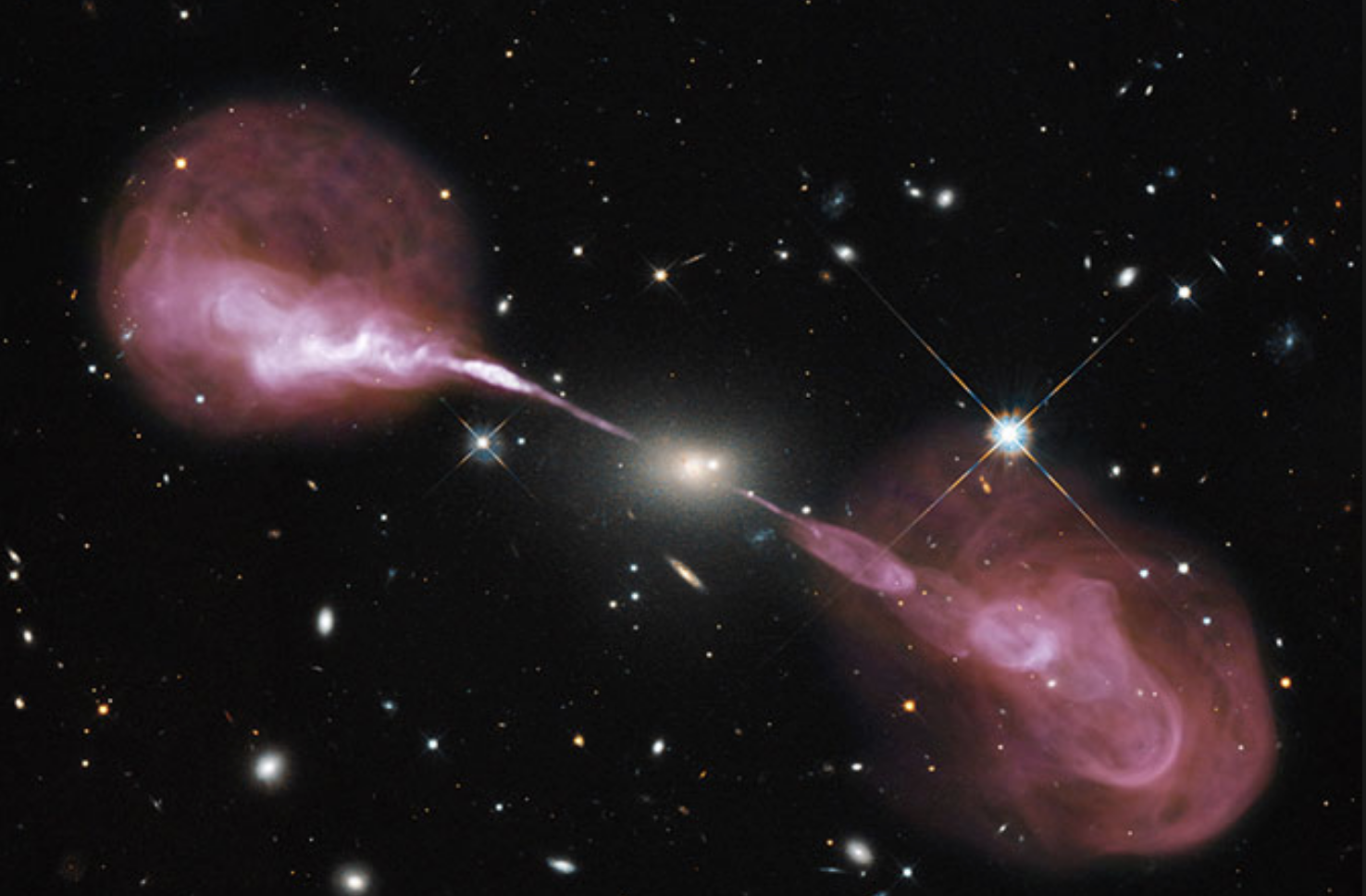

Astrophysical jets are observed in the radio and gamma-ray bands and are thought to be produced be powered by the accretion process and possibly the black hole spin. I use hydrodynamic simulations to model their propagation, particle acceleration and interaction with their environment, in both AGN and X-ray binary systems.
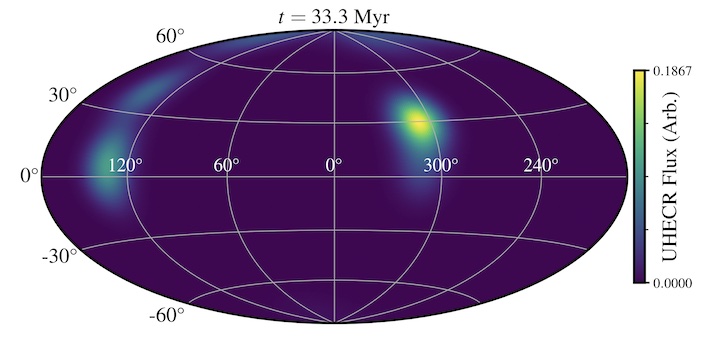
It is not yet understood where the highest energy cosmic rays originate. One of my main research goals is to figure out whether jets from AGN can accelerate the highest energy cosmic rays. More info here.
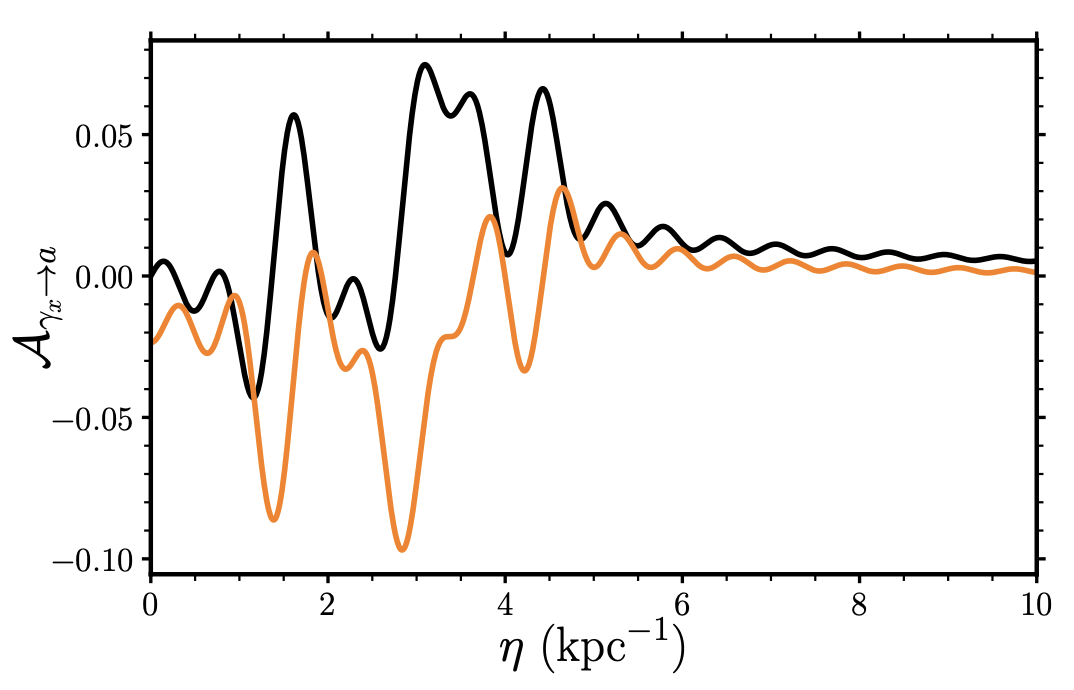
Astrophysical searches for axions
Axions and Axion-like particles are well-motivated extensions to the standard model, predicted by string theory, and important dark matter candidates. In the presence of external magnetic fields, axions and photons can interconvert, a property that can be used to search for axions with astrophysical observations. In particular, I am interested in novel techniques for modelling the axion-photon conversion process and using X-ray observations to search for evidence of axions. Currently, our group's work places the world-leading limits on axions with masses below 1e-11 eV or so.
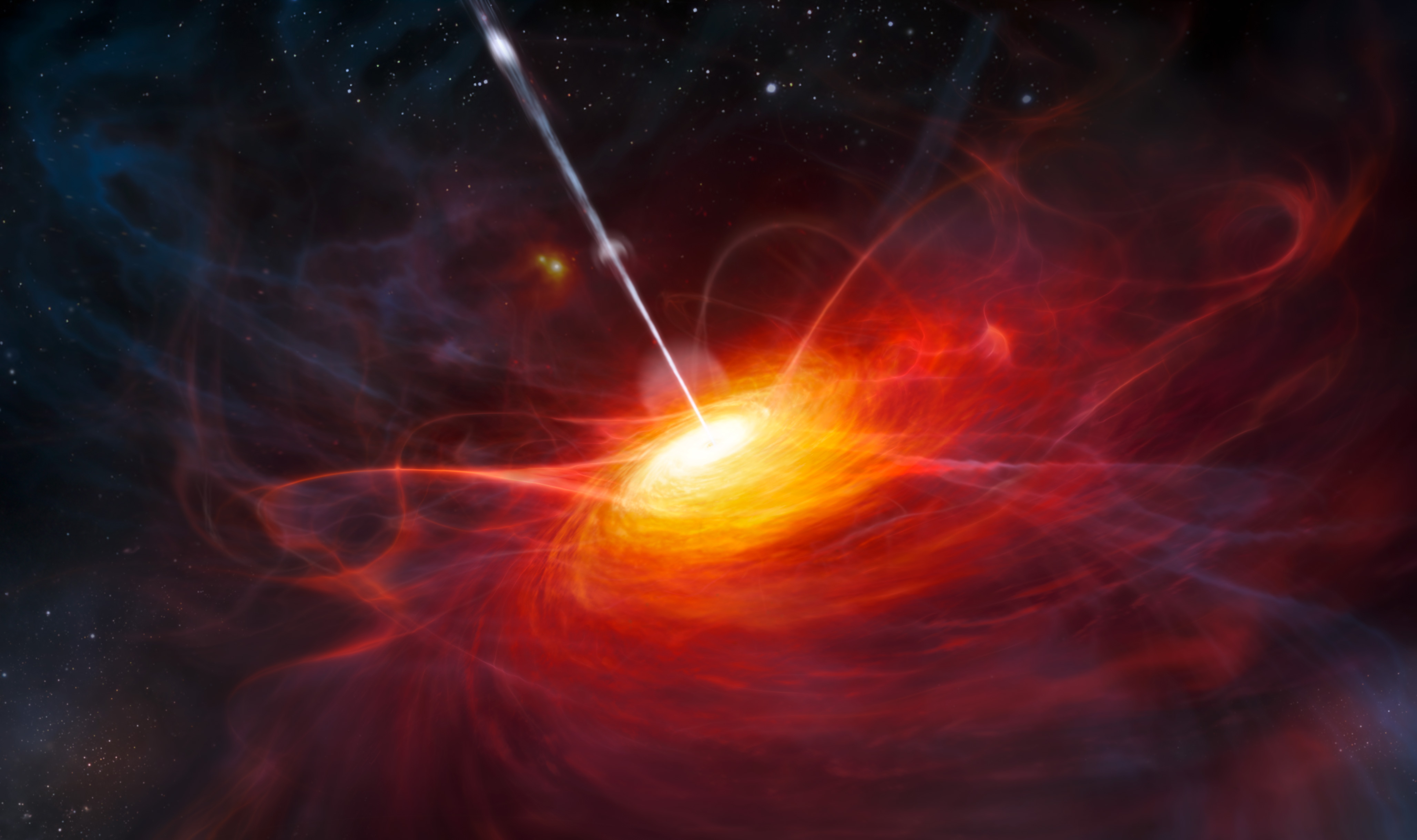

Disc Winds in Accreting Systems
Disc Winds are ubiquitous in accreting systems. I spent my PhD developing a Monte Carlo radiative transfer and photoionization code, and used it to synthesize spectra of accreting objects with associated outflows. I continue to work on disc winds in AGN, X-ray binaries and accreting white dwarfs and I'm particularly fascinated by the physics and driving mechanisms of the outflows.

My public engagement work has involved taking a huge inflatable planetarium into local schools, activities with the homeless in Oxford, the SETI Cipher Challenge and the #AstroAirport. I also enjoy giving public talks on alien life, axions, cosmic rays and black holes. You can check out my public YouTube talks for Astronomy on Tap and Cambridge Astronomy.
Here are some of my favourite papers. You can find a full list of publications on ADS.
SIROCCO: A Publicly Available Monte Carlo Ionization and Radiative Transfer Code for Astrophysical Outflows
2024
Matthews, J. H., Long, K. S., Knigge, C., et al.,
MNRAS, submitted, arXiv:2410.19908
Getting More Out of Black Hole Superradiance: a Statistically Rigorous Approach to Ultralight Boson Constraints
2023
Hoof, S, Marsh, D. J. E., Sisk-Reynes, j, Matthews, J. H., Reynolds, C.
MNRAS, submitted, arXiv:2406.10337
Studying the link between radio galaxies and AGN fuelling with relativistic hydrodynamic simulations of flickering jets
2023
Whitehead, H. W., Matthews, J. H.
MNRAS, 543, 2478
How, where and when do cosmic rays reach ultrahigh energies?
2023
Matthews, J. H., Taylor A. M.
PoS(ECRS)010
The origin of optical emission lines in the soft state of X-ray binary outbursts: the case of MAXI J1820+070
2023
Koljonen, K., Long K. S., Matthews, J. H., Knigge, C.
MNRAS, 521, 4190
Testing AGN outflow and accretion models with C IV and He II emission line demographics in z ≈ 2 quasars
2023
Temple, M. J., Matthews, J. H., Hewett, P. C. et al.
MNRAS, 523, 646
New constraints on light axion-like particles using Chandra transmission grating
spectroscopy of the powerful cluster-hosted quasar H1821+643
2022
Sisk-Reynes, J., Matthews, J. H., Reynolds, C. S., et al.
MNRAS, 510, 1264
A persistent ultraviolet outflow from an accreting neutron star binary transient
2022
Castro Segura, N. et al. (including Matthews, J. H.)
Nature, 603, 52
Echoes of the past: ultra-high-energy cosmic rays accelerated by radio galaxies,
scattered by starburst galaxies
2022
Bell, A. R., Matthews, J. H.
MNRAS, 511, 488
Fourier formalism for relativistic axion-photon conversion with astrophysical applications
2022
Marsh, M. C. D., Matthews, J. H., Reynolds C.~S., Carenza, P.
Phys Rev D, 105, 6013
How Do Magnetic Field Models Affect Astrophysical Limits on Light Axion-like Particles?
An X-Ray Case Study with NGC 1275
2022
Matthews, J. H., Reynolds C.S., Marsh M.C.D., Sisk-Reynes J., Rodman P. E.
ApJ, 930, 90.
Particle acceleration in radio galaxies with flickering jets: GeV electrons to ultrahigh energy cosmic rays
2021
Matthews, J. H., Taylor, A. M.
MNRAS, 503, 5948
Placing LOFAR-detected quasars in C IV emission space: implications for winds, jets and star formation
2021
Rankine, A. L.Matthews, J. H., Hewett, P. C., Banerji, M., Morabito L. K., Richards, G. T.
MNRAS, 502, 4154
Particle acceleration in astrophysical jets
2020
Matthews, J. H., Bell, A. R.; Blundell, K. M..
New AStronomy Reviews, 89, 101543
Stratified disc wind models for the AGN broad-line region: ultraviolet, optical and X-ray properties
2020
Matthews, J. H., Knigge, C., Higginbottom, N., Long, K. S., et al.,
MNRAS, 492, 5540
Hot, dense He II outflows during the 2017 outburst of the X-ray transient Swift J1357.2-0933
2019
Charles, P., Matthews, J. H., Buckley, D., Gandhi P.; Kotze, E.; Paice, J.
MNRAS Letters in press.
Cosmic ray acceleration by shocks: spectral steepening due to turbulent magnetic field amplification
2019
Bell, A., Matthews, J. H., Blundell, K.
MNRAS, 488, 2466.
Ultra-high energy cosmic rays from shocks in the lobes of radio galaxies
2019
Matthews, J. H., Bell, A., Blundell, K., Araudo, A.,
MNRAS, 482, 4303, arXiv:1810.12350
Fornax A, Centaurus A other radio galaxies as sources of ultra-high energy cosmic rays
2018
Matthews, J. H., Bell. A., Blundell, K., Araudo, A.,
MNRAS Letters, 479, 76
Radiation-hydrodynamic simulations of thermally driven disc winds in X-ray binaries
2017
Higginbottom, N., Knigge, C., Long, K. S. Matthews, J. H., et al.,
MNRAS, 479, 3651
Cosmic Ray Acceleration by Relativistic Shocks: Limits and Estimates
2018
Bell. A., Araudo, A., Matthews, J. H., Blundell, K.
MNRAS, 473, 2364
Quasar emission lines as probes of orientation:
implications for disc wind geometries and unification
2017
Matthews, J. H.; Knigge, C.; Long, K. S.
MNRAS, 467, 2571
The reverberation signatures of rotating disc winds in active galactic nuclei
2017
Mangham, S. W., Knigge, C., Matthews, J. H.; Long, K. S.; Sim, S. A.; Higginbottom, N.,
MNRAS, in press, DOI:10.1093/mnras/stx1863
Testing Quasar Unification: Radiative Transfer in Clumpy Winds
2016
Matthews, J. H.; Knigge, C.; Long, K. S.; Sim, S. A.; Higginbottom, N.. Mangham, S. W.
MNRAS, 458, 293
The impact of accretion disc winds on the optical spectra of cataclysmic variables
2015
Matthews, J. H.; Knigge, C.; Long, K. S.; Sim, S. A.; Higginbottom, N.
MNRAS,
450,
3.
Line-driven Disk Winds in Active Galactic Nuclei: The Critical Importance of Ionization and Radiative Transfer
2014
Higginbottom, N.; Proga, D.; Knigge, C.; Long, K. S.; Matthews, J. H.; Sim, S. A.
The Astrophysical Journal,
789,
1.
Invited Review: Sources of UHECRs
July 2022
European Cosmic Ray Symposium, Nijmegen
Invited Review: Particle acceleration in AGN jets
July 2022
EuCAPT Symposium, Remote
Jet Modelling in Radio-Loud AGN
July 2022
EAS 2020, Remote
Invited Talk: Particle Acceleration in Jets
July 2019
A Centenary of Jets, Jodrell Bank
Invited Review: Disc Winds in Accreting White Dwarfs
July 2019
From Winds to Jets, Amsterdam
Invited Talk: UHECRs from Radio Galaxies
December 2018
Hillas Symposium, Heidelberg
Invited Talk: UHECRs from Radio Galaxies
November 2018
Particle Acceleration Conference, Calabria
Contributed Talk: UHECRs from Radio Galaxies
November 2018
UHECR 2018, Paris
Invited Colloquia: UHECRs from Radio Galaxies
2017-2018
Belfast, Manchester, Nottingham, Oxford, Southampton
Testing Quasar Unification with Radiative Transfer Simulations
June 2017
AGN Winds on the Georgia Coast, Jekyll Island, GA
Invited Review: Ultraviolet Astronomy
March 2017
Broadband Astrophysical Processes, Southampton
Modelling the Spectra of Quasars: Clumpy Winds and Unification
September 2015
TORUS 2015, Winchester, UK
Disc Winds Matter! Their impact on the optical spectra of cataclysmic variables
September 2015
The Golden Age of Cataclysmic Variables, Palermo, Italy
Modelling the Spectra of Quasars: Clumpy Winds and X-ray Properties
June 2015
The Extremes of Black Hole Accretion, Madrid, Spain
Modelling the Spectra of Quasars: Clumpy Winds and X-ray Properties
June 2015
Black Hole Accretion and AGN Feedback, Shanghai, China
Public Talk- The Search For Alien Life
2015
Stargazing Live on campus event, University of Southampton
Modelling the Spectra of Quasars
June 2014
Accretion Disc Winds Meeting, Durham, UK
The Impact of Disc winds on the optical spectra of Cataclysmic Variables
2012
Cataclysmic Variables Meeting, Columbia University, New York
Searching for Nearby Planets During Predicted Mesolensing Events
2012
Exoplanet Lunch, Harvard CfA, USA
Systematic Exoplanet Searches During Predicted Mesolensing Events [POSTER]
2012
American Astronomical Society, AAS Meeting